 Prior posts on this blog have discussed the general aspects of property partition actions. A partition action arises when there are two or more owners of real property, and the co-owners cannot agree on the disposition of the property. The property may be residential or commercial in nature. This blog post will discuss possible out-of-court resolutions to a partition action.
Prior posts on this blog have discussed the general aspects of property partition actions. A partition action arises when there are two or more owners of real property, and the co-owners cannot agree on the disposition of the property. The property may be residential or commercial in nature. This blog post will discuss possible out-of-court resolutions to a partition action.
A partition action may be brought by any of the co-owners to force a sale of the property, with the proceeds being divided among the owners according to their percentage of ownership. However, it is a fact that most lawsuits are settled prior to trial or another resolution by a Court. In a partition action, there are several alternatives to explore when deciding to resolve a case without the need for further Court intervention.
The first alternative would be for the parties to agree to sell the property to a third party who is not one of the current co-owners. In such a situation, the co-owners should agree on sale terms, and, in most situations, hire a professional real estate broker to list and show the property in question. The parties would also agree to share the costs of the broker, which is usually a set percentage of the sales price. It is advisable at this stage that a formal written agreement, usually called a “Stipulation of Settlement,” be entered into between the parties. Such an agreement should contain an initial listing price for the property. It should also state that any offer at or above the listing price will be accepted by all of the owners. In the event that the property cannot be sold at or above the listing price, the agreement should also delineate a set period of time in which the parties will attempt to sell the property at the initial listing price, such as three months. After this time period expires, the agreement should state that the listing price will be reduced by a set percentage, such as five percent. This will allow the property to be sold at a price acceptable to all parties, and will prevent any co-owner from refusing to sell the property. Our firm has handled many partition actions and has a standard Stipulation of Settlement that contains the necessary clauses for an effective resolution.
 New York Real Estate Lawyers Blog
New York Real Estate Lawyers Blog


 As stated in a
As stated in a As we enter the last days of summer,
As we enter the last days of summer, It is not unusual for the estate of a deceased person to hold stock as an asset. Stock can take the form of shares held in a publically traded company, such as Target, or shares in a cooperative corporation. Clients often ask
It is not unusual for the estate of a deceased person to hold stock as an asset. Stock can take the form of shares held in a publically traded company, such as Target, or shares in a cooperative corporation. Clients often ask 
 Many of our clients are landlords who own only one property, such as a single or multi-family house or an apartment. Although they may be renting to a tenant, it is not their primary business or livelihood. As such,
Many of our clients are landlords who own only one property, such as a single or multi-family house or an apartment. Although they may be renting to a tenant, it is not their primary business or livelihood. As such,  A recent
A recent  Parties to real estate transactions often ask
Parties to real estate transactions often ask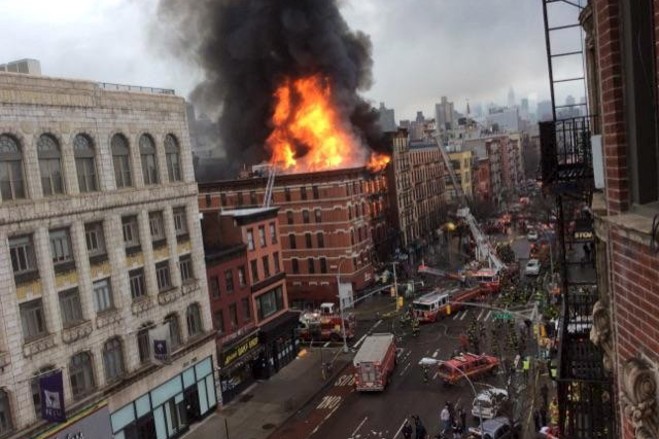  A
A