 New Yorkers seem to be “taxed to death”, paying the highest average property taxes in the country. We are the only state that charges a tax for the making of a mortgage. The tax burden does not end at death, as New York also has its own estate tax. Governor Andrew Cuomo, seeking re-election this year, has been encouraging the state legislature to reduce these burdens.
New Yorkers seem to be “taxed to death”, paying the highest average property taxes in the country. We are the only state that charges a tax for the making of a mortgage. The tax burden does not end at death, as New York also has its own estate tax. Governor Andrew Cuomo, seeking re-election this year, has been encouraging the state legislature to reduce these burdens.
Estates may be subject to both federal and state estate taxes. During the past thirteen years, the federal estate tax has been modified. The federal taxable exemption now stands at a generous amount of $5,340,000.00 per person. This generally means that estates that do not exceed this amount are not subject to federal estate taxes. As many people do not have estates that exceed such amount, federal estate tax is not a concern for most families. However, New York State has levied an estate tax on estates exceeding $1,000,000.00 until a revision to the law was passed in April of this year. Since many New Yorkers could easily have assets exceeding $1,000,000.00, considering high property values, many of our residents have been subject to state estate tax.
The revision to New York’s estate tax law now provides that the exemption will immediately rise to $2,062,500.00, so that only estates valued above that amount will be subject to New York state estate taxes. Further, each April, the state estate tax exemption is set to rise by $1,062,500.00, until it reaches $5,250,000.00 in 2017, then the exemption will continue to rise to close to $6,000,000.00 on January 1, 2019. Tax liability will certainly be a “moving target” during the next five years.
 New York Real Estate Lawyers Blog
New York Real Estate Lawyers Blog



 The Associated Press recently reported about a
The Associated Press recently reported about a 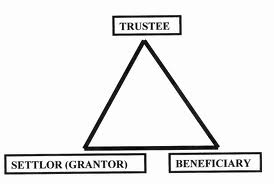 In
In  Trusts provide a valuable tool in estate planning because they serve the purposes of preserving assets, protecting intended beneficiaries, and potentially saving or eliminating estate taxes. A trust is a legal document that conveys a “corpus”, or body of assets, from the settlor (the person who creates the trust and owns to assets) to a trustee (the individual or corporate entity with the responsibility of holding the assets) for the benefit of the beneficiary (the person who will ultimately receive the proceeds of the trust). A charitable organization may also be the beneficiary of a trust.
Trusts provide a valuable tool in estate planning because they serve the purposes of preserving assets, protecting intended beneficiaries, and potentially saving or eliminating estate taxes. A trust is a legal document that conveys a “corpus”, or body of assets, from the settlor (the person who creates the trust and owns to assets) to a trustee (the individual or corporate entity with the responsibility of holding the assets) for the benefit of the beneficiary (the person who will ultimately receive the proceeds of the trust). A charitable organization may also be the beneficiary of a trust.  From time to time,
From time to time,  The fiftieth anniversary of the March on Washington was recently acknowledged, celebrating the great civil rights battle for equality for our African-American citizens. More recently, same-sex couples have also been engaged in their own battle for equal treatment in issues such as the right to marry, taxation, health and pension benefits, and similar property and economic matters.
The fiftieth anniversary of the March on Washington was recently acknowledged, celebrating the great civil rights battle for equality for our African-American citizens. More recently, same-sex couples have also been engaged in their own battle for equal treatment in issues such as the right to marry, taxation, health and pension benefits, and similar property and economic matters.  Our readers may be aware of an
Our readers may be aware of an  Our readers who follow politics know that members of Congress have battled in recent years with respect to revisions to the tax law. Specifically, estate, gift, and income taxes have been subject to adjustments. The purpose of this blog post is not to describe the
Our readers who follow politics know that members of Congress have battled in recent years with respect to revisions to the tax law. Specifically, estate, gift, and income taxes have been subject to adjustments. The purpose of this blog post is not to describe the  This blog post contains a description of some of the standard substantive objections that a person may have to the admission of a Will to probate.
This blog post contains a description of some of the standard substantive objections that a person may have to the admission of a Will to probate.